NAT exemption
When internet edge devices have a site-to-site VPN configured on an interface and also have NAT rules for that interface, you must exempt the VPN traffic from the NAT rules. If you do not exempt the VPN traffic from NAT translation, the traffic gets dropped or is not routed through the VPN tunnel to the remote peer.
NAT exemption allows you to exclude traffic from being translated by NAT rules. When you create a policy-based site-to-site VPN using the Firewall Management Center VPN wizard, you can select the NAT Exempt option to create the rules automatically (). By default, this option is enabled. You can view the NAT exemptions for a device in the NAT policy page (, and then click NAT Exemptions).
The Firewall Management Center supports NAT exemption for all policy-based site-to-site VPN topology types. For more information, see Configure a Policy-based Site-to-Site VPN.
Consider the following example, which shows a site-to-site VPN tunnel connecting Site A and Site B. For traffic that must go to the Internet, NAT translates the private IPs to a public IP address to access the Internet. For traffic that must go over the VPN tunnel, you must configure NAT exemption for the device in the VPN wizard.
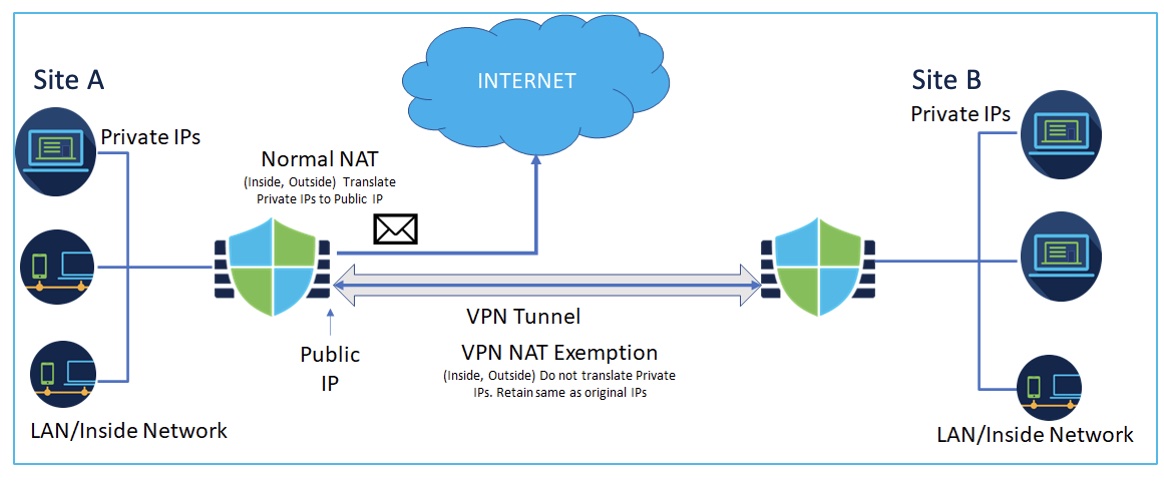
Note that when you upgrade from versions earlier than 7.4, if you have enabled NAT exemption, Firewall Management Center will disable this option. You must enable this option in the policy-based site-to-site VPN wizard.