Guidelines and Limitations for Instances
General Guidelines
-
A single Firewall Management Center must manage all instances on a chassis, as well as manage the chassis itself.
-
For instances, the following features are not supported:
-
TLS crypto acceleration
-
Clustering
-
Firewall Management Center UCAPL/CC mode
-
Flow offload to hardware
-
LLDP
-
-
Primary management of the chassis by Security Cloud Control cloud-delivered Firewall Management Center and separate analytics-only management of the chassis by an on-prem Firewall Management Center is not supported. You can however add Security Cloud Control-managed instances to an analytics-only on-prem Firewall Management Center.
Management Interface
-
No support for a data interface for chassis management; only the dedicated Management interface can be used
-
No DHCP addressing for the Management interface
-
The management connection requires TCP port 8305; do not change the value from the default.
VLAN Subinterfaces
-
This document discusses chassis VLAN subinterfaces only. You can separately create subinterfaces within the instance.
-
If you assign a parent interface to an instance, it only passes untagged (non-VLAN) traffic. Do not assign the parent interface unless you intend to pass untagged traffic.
-
Subinterfaces are supported on Data or Data-sharing type interfaces.
-
You can create up to 500 VLAN IDs.
-
You cannot use subinterfaces for an inline set or as a passive interface.
-
If you use a subinterface for the failover link, then all subinterfaces on that parent, and the parent itself, are restricted for use as failover links. You cannot use some subinterfaces as failover links, and some as regular data interfaces.
EtherChannels
-
You can configure up to 48 EtherChannels, limited by the number of physical interfaces.
-
The EtherChannel can have up to 8 active interfaces.
-
All interfaces in the EtherChannel must be the same media type and speed capacity. The media type can be either RJ-45 or SFP; SFPs of different types (copper and fiber) can be mixed. You cannot mix interface capacities (for example 1GB and 10GB interfaces) by setting the speed to be lower on the larger-capacity interface, unless you set the speed to Detect SFP; in this case, you can use different interface capacities, and the lowest common speed is used.
-
The chassis does not support LACPDUs that are VLAN-tagged. If you enable native VLAN tagging on the neighboring switch using the Cisco IOS vlan dot1Q tag native command, then the chassis will drop the tagged LACPDUs. Be sure to disable native VLAN tagging on the neighboring switch.
-
In Cisco IOS software versions earlier than 15.1(1)S2, the chassis did not support connecting an EtherChannel to a switch stack. With default switch settings, if the chassis EtherChannel is connected cross stack, and if the primary switch is powered down, then the EtherChannel connected to the remaining switch will not come up. To improve compatibility, set the stack-mac persistent timer command to a large enough value to account for reload time; for example, 8 minutes or 0 for indefinite. Or, you can upgrade to more a more stable switch software version, such as 15.1(1)S2.
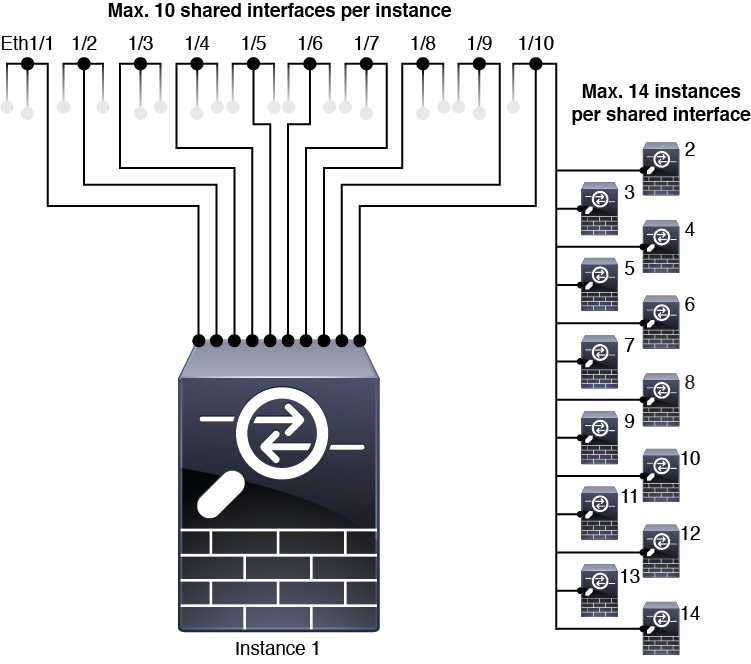
Data-sharing Interfaces
Maximum 14 instances per shared interface. For example, you can allocate Ethernet1/1 to Instance1 through Instance14.
Maximum 10 shared interfaces per instance. For example, you can allocate Ethernet1/1.1 through Ethernet1/1.10 to Instance1.
-
You cannot use a data-sharing interface with a transparent firewall mode instance.
-
You cannot use a data-sharing interface with inline sets or passive interfaces.
-
You cannot use a data-sharing interface for the failover link.
Default MAC Addresses
-
MAC addresses for all interfaces are taken from a MAC address pool. For subinterfaces, if you decide to manually configure MAC addresses, make sure you use unique MAC addresses for all subinterfaces on the same parent interface to ensure proper classification. See Automatic MAC Addresses for Instance Interfaces.