Perform a Ping on the Cluster Control Link
When a node joins the cluster, it checks MTU compatibility by sending a ping to the control node with a packet size matching the cluster control link MTU. If the initial ping fails, the node tries a ping using a smaller packet size (the MTU divided by 2, then by 4, then by 8) until a ping succeeds. A notification is generated so you can fix the MTU mismatch on connecting switches and try again. This tool lets you manually ping all nodes that have already joined the cluster in case you are having cluster control link connectivity problems.
You can check to make sure all the cluster nodes can reach each other over the cluster control link by performing a ping. One major cause for the failure of a node to join the cluster is an incorrect cluster control link configuration; for example, the cluster control link MTU may be set higher than the connecting switch MTUs.
Procedure
Step 1 | Choose , click the More ( 
|
Step 2 | Expand one of the nodes, and click CCL Ping. 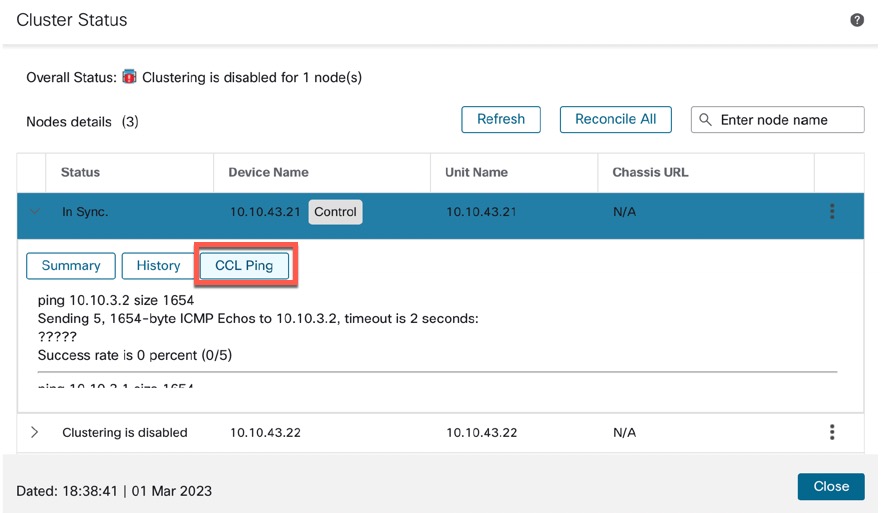
The node sends a ping on the cluster control link to every other node using a packet size that matches the maximum MTU. |
