Multicloud Defense Egress Gateways
Egress/East-West
Deploying an Egress/East-West gateway to protect traffic leaving their public cloud networks. The egress gateway functions as a transparent forward proxy, performing full decryption and embedding advanced security features like intrusion prevention, antimalware, data loss prevention, and full-path URL filtering. Optionally, it can also operate in a forwarding mode, where it doesn't proxy or decrypt traffic but still applies security functionalities like malicious IP blocking and FQDN filtering.
The diagram is an example of an AWS account with an egress gateway in a centralized mode:
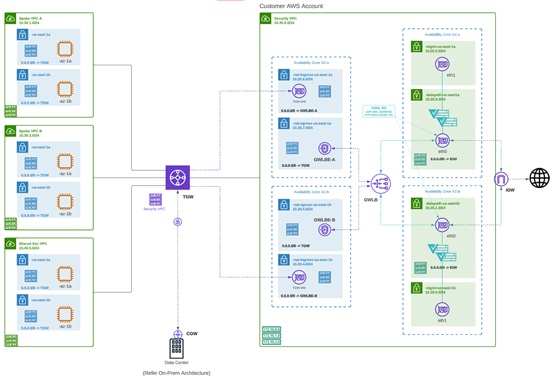
NAT Gateways in Egress
Note | At this time, Multicloud Defense supports native gateways in an egress deployment for AWS and Azure ony. |
Network Address Translation (NAT) gateways are gateways designed to originate from within your cloud service provider. Egress traffic appears from a single IP address, or at least one per availability zone. By building a gateway and hosting it from within your cloud environment you can potentially increase efficiency and reduce costs. Note that if the association between the VPC or VNet in Multicloud Defense and the gateway in your cloud service provider fails, Multicloud Defense system logs capture the instance for troubleshooting.
These are the configurations that are supported:
-
Azure supports one subnet.
-
You must have at least one public IP address configured in your NAT gateway.
The diagram is an example of an Azure account with an egress gateway in a centralized mode:
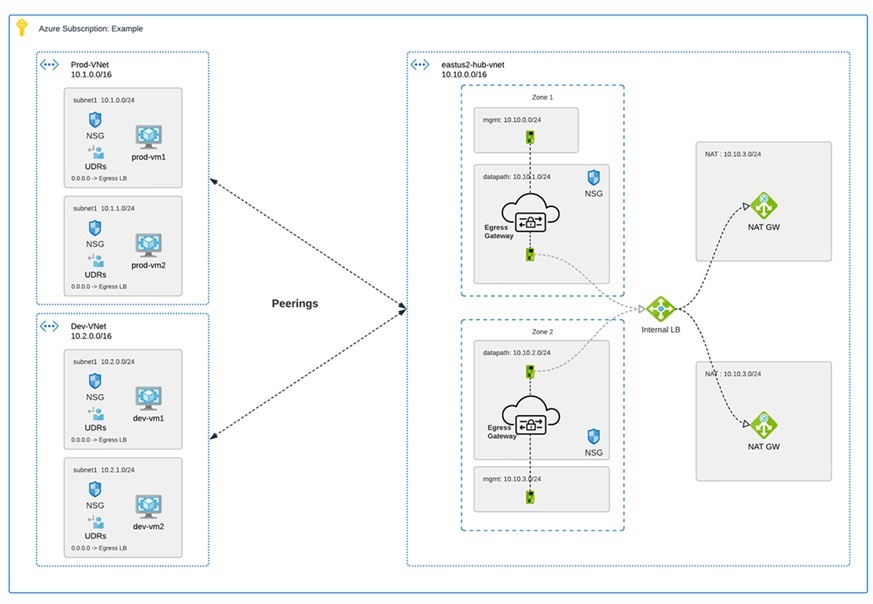
AWS CloudWAN
At this time, Multicloud Defense supports the inclusion of AWS' CloudWAN in egress gateways. CloudWAN is an intent-driven managed wide area network (WAN) service that unifies your data center, branch, and AWS networks. While it is possible to create a global network by interconnecting multiple Transit Gateways across regions, CloudWAN offers built-in automation, segmentation, and configuration management features specifically designed for building and operating global networks based on your core network policy.
This option provides enhanced features such as automated VPC attachments, integrated performance monitoring, and centralized configuration, all managed within AWS Network Manager. This enables you to centrally manage and visualize your CloudWAN core network and Transit Gateway networks across AWS accounts, regions, and on-premises locations.
Key Benefits:
-
Simplified Network Management: AWS CloudWAN provides a centralized dashboard through AWS Network Manager for managing network configurations, policies, and monitoring traffic. This greatly reduces the complexity of dealing with multiple, disparate networking solutions and offers a unified view of the network.
-
Scalability: It enables customers to easily scale their network as their business grows. As organizations expand their cloud presence and global footprint, CloudWAN can accommodate the increased demand without requiring significant manual reconfiguration
-
Optimized Performance: By leveraging AWS’s global infrastructure, CloudWAN ensures high performance and low latency connectivity across various geographic locations, improving application performance and user experience.
CloudWAN Simplification:
-
Centralized Policy Management: The core network policy, written in a declarative language, defines segments, AWS region routing, and how attachments should map to segments. With a single network policy, customers can manage their entire network’s routing and security policies, reducing the need for manual configurations and minimizing errors.
-
Automated Operations: CloudWAN automates many network management tasks, such as route propagation and policy enforcement, freeing up IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
-
Seamless Integration: It integrates with other AWS services and third-party solutions, enabling customers to build a cohesive and comprehensive network infrastructure with minimal friction.
-
Enhanced Visualization: AWS Network Manager provides several dashboard visualizations, including world maps pinpointing network resources, monitoring with CloudWatch events, real-time event tracking, and topological diagrams of your network. This makes it easier to manage and monitor all aspects of your global network.
Security service insertion refers to the practice of integrating security services directly into the network path. Here are the benefits of implementing this with Multicloud Defense:
-
Enhanced Security Posture: By inserting security services into the network, traffic can be inspected, monitored, and filtered in real-time, ensuring that threats are detected and mitigated before they can impact critical resources.
-
Consistent Security Policies: Security service insertion ensures that consistent security policies are applied across the entire network, regardless of the underlying infrastructure or geographic location. This uniformity simplifies compliance and governance.
-
Improved Visibility and Control: Integrating security services provides enhanced visibility into network traffic and potential threats. Administrators can leverage advanced analytics and monitoring tools to gain deeper insights and more effectively manage security risks.
-
Reduced Latency and Complexity: By embedding security functions into the network path rather than routing traffic through separate security appliances, latency is minimized, and network complexity is reduced, leading to better performance and simpler network architecture.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: Security service insertion with Multicloud Defense enables organizations to dynamically scale their security measures in response to changing network conditions and emerging threats, ensuring robust protection at all times.
-
Centralized Security: Consolidates security resources, reducing management burden and saving on infrastructure costs.
-
Simplified Routing: Easily steer network traffic to security appliances without complex routing configurations or third-party automation tools.
-
Multi-Region Security Inspection: Simplifies multi-region deployments, allowing intra-region and inter-region traffic to pass through security infrastructure without complex configurations.
By leveraging AWS CloudWAN and Multicloud Defense for security service insertion, customers can achieve a high-performing, secure, and easily manageable network infrastructure that supports their business growth and operational resilience. Multicloud Defense allows users to create a security services VPC, attach it to an existing CloudWAN, create a Network Functions Group (NFG), and secure spoke segments by updating routing—all in an automated manner.
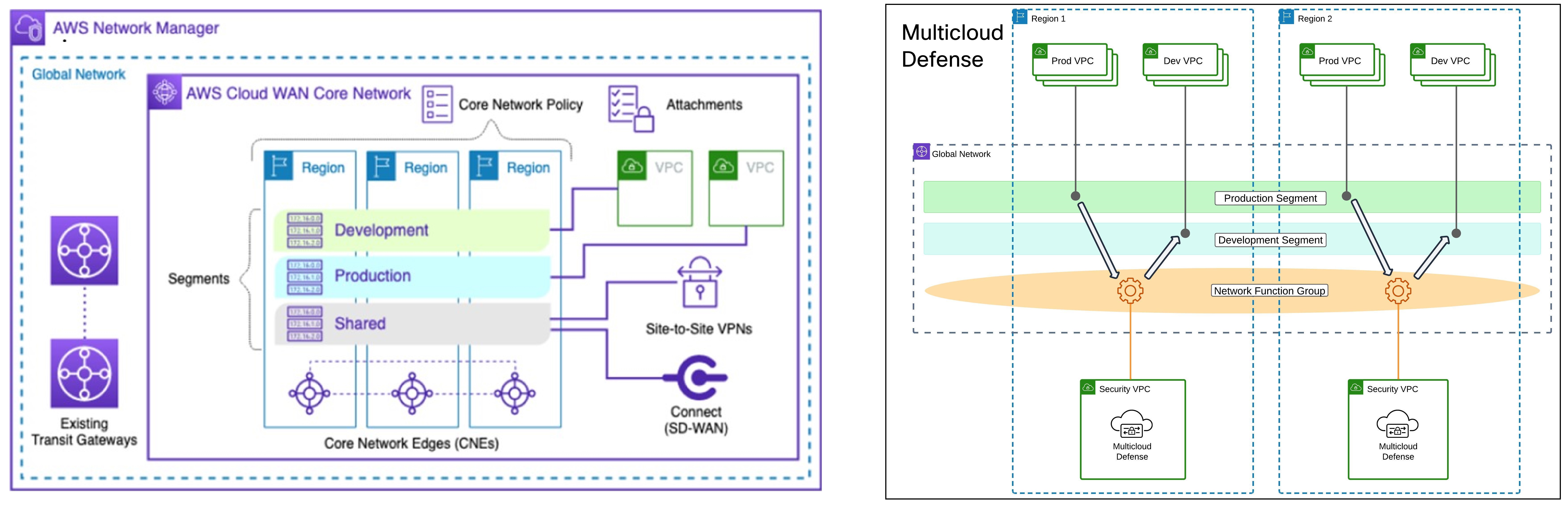
How to Create a Service VPC with AWS CloudWAN
To successfully create a service VPC with AWS CloudWAN, follow these steps:
-
Create Service VPCs: Establish service VPCs in multiple CNEs with required gateways.
-
Create Network Function Groups (NFGs).
-
Attach Service VPCs as NFGs: Use attachment policy rules to attach service VPCs.
-
Attach Workload VPCs: Attach VPCs to respective segments using attachment policy rules.
-
Update Routing: Modify policies and Workload VPCs to update the routing.
-
Update Core Network Policies: Apply and execute the required changes in the Core Network policies.
Consider the following limitations before you create a service VPC with AWS CloudWAN:
-
NAT gateways are mandatory for service VPCs.
-
Dual-Hop and Edge Selection is currently not supported.
-
Due to a limitation in AWS CloudWAN limitation that does not support SNAT-enabled traffic for forwarding, traffic drops for policy rulesets configured with SNAT. We strongly recommend you disable SNAT in your Multicloud Defense policy ruleset.
-
To add an additional service VPCs in different regions (CNE) use one of the two options:
-
Manual execution and application of policies are needed to update the routing for the new NFG attachment.
-
Manually update the routing tables of new service VPC datapath subnets with workload VPC routes through the Core Network.
-